The Frequency.
The Frequency (symbol f), most often measured in hertz (symbol: H z), is the number of occurrences, of a repeating event per unit of time.
It is also occasionally referred, to as temporal frequency, for clarity, and to distinguish it, from spatial frequency.
Ordinary frequency is related, to angular frequency, (symbol ω, with SI unit radian per second) by a factor of 2π.
The period (symbol T), is the interval of time between events, so the period is the reciprocal of the frequency: T = 1/f.
The Frequency is an important parameter, used in science, and engineering, to specify the rate of oscillatory, and vibratory phenomena.
such as mechanical vibrations, audio signals (sound), radio waves, and light.
Example:
if a heart beats, at a frequency of 120 times per minute, (2 hertz).
The period - the interval between beats, is half a second, (60 seconds divided by 120 beats).
Definitions and units.
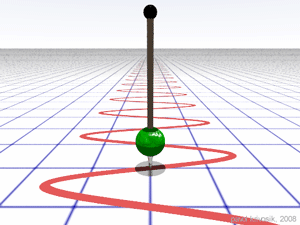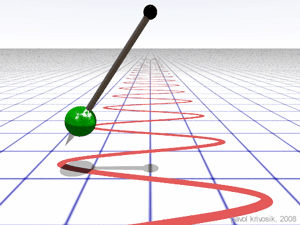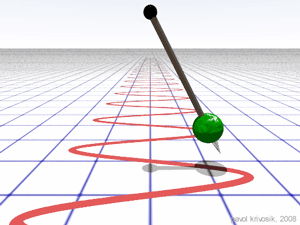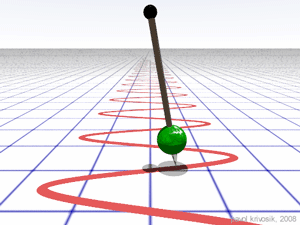
A pendulum with a period of 2.8 second, and a frequency of 0.36 Hz.
For cyclical phenomena such as oscillations, waves,
or For examples of simple harmonic motion.
The term frequency is defined, as the number of cycles, or repetitions per unit of time.
The conventional symbol, for frequency is f, or ν (the Greek letter nu), is also used.
The period T, is the time taken to complete, one cycle of an oscillation, or rotation.
The frequency, and the period are related by the equation.
f = 1/T .
{\displaystyle f={\frac {1}{T}}.}
The term temporal frequency is used, to emphasise that the frequency is characterised, by the number of occurrences, of a repeating event per unit time.
The SI unit of frequency is the hertz (Hz).
The Sound.
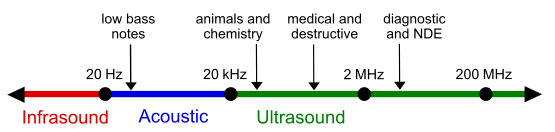
The sound wave spectrum, with rough guide of some applications.
The Sound propagates, as mechanical vibration waves of pressure, and displacement, in air, or other substances.
In general, frequency components of a sound, determine its "color", its timbre.
When speaking, about the frequency, (in singular) of a sound, it means the property, that most determines its pitch.
The frequencies an ear of the human, can hear are limited, to a specific range of frequencies.
The audible frequency range, for the humans is typically given as, being between about 20 Hz and 20000 Hz (20 kHz).
Though, the high frequency limit, usually reduces with age.
Other species have different hearing ranges.
Example:
some dog breeds can perceive vibrations up to 60000 Hz.
In many media, such as air, the speed of sound is approximately, independent of frequency, so the wavelength of the sound waves, (distance between repetitions) is approximately, inversely proportional to frequency.
The Human Voice in the Universe or the Space or the outside planet Earth.
No, a human voice does not move in the universe or the Space or the outside planet Earth.
The Sound does not travel in the universe or the Space or the outside planet Earth.
The Sound waves travel, through vibrations in a medium, like air or water or solid, and cannot travel through empty space.
In the universe or the Space or the outside planet Earth, there are no atoms or molecules to carry sound waves, so there is no sound.
The Sound waves lose, energy over time.
As they travel through a medium, causing them to get quieter, and quieter until they disappear.
The Sound waves are reflected, by mediums.
Like walls, pillars, and rocks, which is known as an echo.
Can you hear sound in space.
No, you cannot hear any sounds, in near-empty regions of the space.
The Sound travels, through the vibration of atoms, and molecules in a medium, (such as air or water or solid).
In the universe or the Space or the outside planet Earth, where there is no air, sound has no way to travel.
Is it possible, to send messages, through brain waves of the human?.
Technical telepathy is the best method.
The electrical nature of the brain allows, not only for sending of signals, but also for the receiving of electrical pulses.
These can be delivered, in a non-invasive way, using a technique called transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS).
What is the highest brain wave in Humans?.
Gamma brain waves are the fastest brain waves, produced inside human brain.
Although, they can be hard to measure accurately, they tend to measure above 35 Hz, and can oscillate as fast as 100 Hz.
Human brain tends to produce gamma waves.
How to measure brain activity in humans.
The Human Brain, is difficult to study, not only, because of its inherent complexity;
The billions of neurons, the hundreds or thousands of types of neurons, the trillions of connections.
The Human Brain, also works at a number of different scales, both in the physical sense and in the time domain.
To understand, the human brain’s electrical activity at these scales, no single technology is enough.
As a result, neuroscientists have a suite of tools, at their disposal.
Some of these, such as fMRI and EEG, can be used in humans, because they are non-invasive; they work through, by looking into the skull, But, these tools suffer, from a lack of detail.
To get a more microscopic picture, of neuron activity, researchers turn to human models.
This allows the behaviour of individual neurons, or small groups of neurons, to be analysed in much greater detail.
The main Questions, for which this mission exists.
1. The Human Mouth, and The Human Ears are having, fixed distances, and standard range.
2. The Sound speed is, only 343 meter per second.
3. The Diameter of the Planet Earth, is 12756 killometer, that is 1 crore, 27 lakh, 56 thousand, Meter.
4. How, these Voices or Sounds or Noises are listening, at the same time, that is simultaneously, in every corner.
5. How, these Voices or Sounds or Noises are listening, by each & every People, inside all the countries of whole world.
6. How, these Voices or Sounds or Noises are listening, by Peoples, in the universe or Space or outside planet Earth, where no air.
7. Why, these Voices or Sounds or Noises are unknown, generating source.
8. Nobody knows, from where generating, these Voices or Sounds or Noises.
9. First Conclusion is, there is no role of, Human Mouth, and Human Ears.
10. Only one body part, Human Brain is not having, fixed distances, or standard range.
11. The Human Brain is, no clear boundary, for what, it is capable of.
12. The Human Brain will hold, up to 1 quadrillion pieces of information, That is, 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 pieces of information. Till now, no body has confirmed about human brain's storage capacity.
13. Second Conclusion is, there is definitely role of the Human Brain, it is the last option.




 Click below to Listen ...
Click below to Listen ...